Usage
Implementation of the VueMS module itself does not lead to changes in the architecture.
In order to use the new architecture you need to prepare a project for it and adapt to the rules of module creation.
Mixing of these two approaches is allowed.
Installation of required libraries
The first step to the correct operation of VueMS is to install appropriate libraries.
nuxt + vue
VueMS is a Nuxt module so it is obvious that the project should be based on Vue + NuxtJS technology.
@nuxtjs/router
To connect the routing output from the modules you had to use a library that allows you to use your own routing configuration.
You can use your own router.js to handle your routes into your NuxtJS application.
pages/ directory into NuxtJS and will use a router.js file at your srcDir directory.
npm install --save-dev @nuxtjs/router
export default {
buildModules: [
'@nuxtjs/router',
]
}
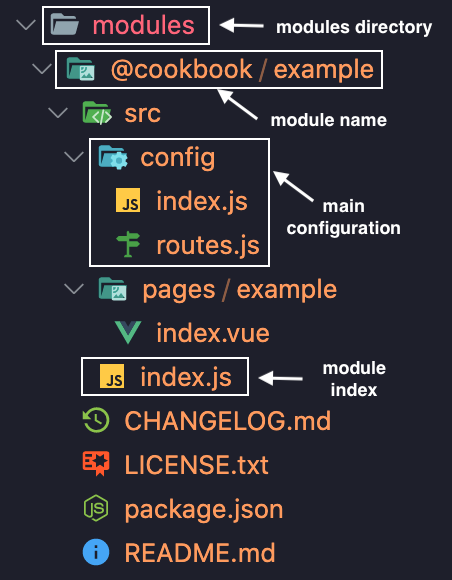
modules directory
Create an modules directory to keep the modules in it.
Directory should be located in the root directory of the project.
Add router
Create router.js file that need to export a createRouter method.
router.js file should be located in the root directory of the project.
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
Vue.use(Router);
export function createRouter() {
return new Router({...})
}
The next step is to load the routing from all modules.
This is done using the extendRoutes method, which is generated by the VueMS library.
extendRoutes method.
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import {
extendRoutes,
} from '~/.nuxt/routerHelper.modules';
Vue.use(Router);
export function createRouter() {
return new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: '/',
routes: extendRoutes(),
});
}
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import {
extendRoutes,
} from '~/.nuxt/routerHelper.modules';
import localRouter from './router.local';
Vue.use(Router);
export function createRouter() {
return new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: '/',
routes: extendRoutes(localRouter),
});
}
Add middleware
Middleware is a built-in NuxtJS mechanism.
By changes in the architecture you have to modify this mechanism.
Global middleware
This type of middleware will be called for every route change.
modulesMiddlewareLoader is an example file name, you can set up what you want.
export default {
router: {
middleware: [
'modulesMiddlewareLoader',
],
},
}
The main middleware must be located in the middleware directory.
It imports a file created by VueMS that runs the global middleware from the modules.
import modulesMiddlewares from '~/.nuxt/middleware.modules';
export default (ctx) => {
modulesMiddlewares(ctx);
};
Local middleware
This type of middleware will be run on specific routing.
To a previously created router.js file you need to add an entry allowing you to add appropriate middleware to the routing.
Use the helper method setLocalMiddlewares, which we use as in the example.
The context given to the setLocalMiddlewares method will be available for all middlewares.
import Vue from 'vue';
import Router from 'vue-router';
import {
extendRoutes,
setLocalMiddlewares,
} from '~/.nuxt/routerHelper.modules';
import localRouter from './router.local';
Vue.use(Router);
export function createRouter() {
const router = new Router({
mode: 'history',
base: '/',
routes: extendRoutes(localRouter),
});
router.beforeEach(
(to, from, next) => setLocalMiddlewares({
to,
from,
next,
}),
);
return router;
}